All available copper-bearing natural mineral aggregates are called copper mines. The high-grade copper concentrate can be obtained by the coarse grinding, roughing, scavenging of copper ore, then grinding and concentrating of coarse concentrate.
Classification of copper ore
Due to the different types of ore, the nature of the ore is also different, so the beneficiation process needs to be customized. The specific process for selecting copper ore depends mainly on the material composition, structure and copper occurrence state of the original copper ore.
Generally speaking, copper ore can be divided into three categories: copper sulfide ore, copper oxide ore and natural copper.
| Types | Minerals |
| Copper sulfide ore | chalcopyrite, bornite and chalcocite, etc. |
| Copper oxide ore | cuprite, malachite, azurite, silicon malachite, etc. |
| Natural copper | little natural copper in nature |
Copper ore beneficiation methods
Before the beneficiation of copper ores, crushing and grinding are required. The bulk ores are crushed to about 12cm by a jaw crusher or a cone crusher. Then the crushed materials are sent to the grinding equipment, and the final particle size of the copper ore is reduced to 0.15-0.2mm.
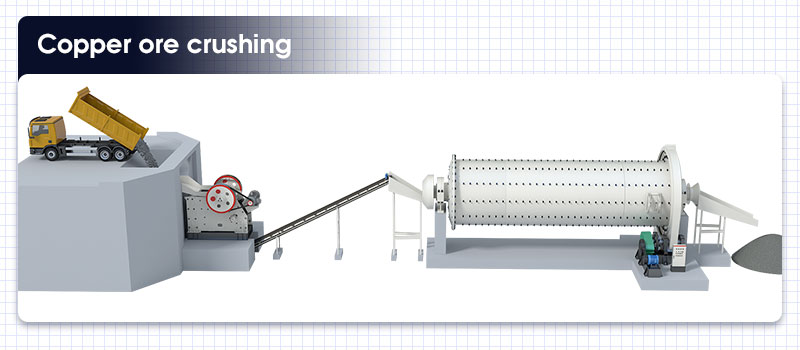
Copper ore crushing process
1. Beneficiation methods of copper sulfide ore
Copper sulfide can be divided into single copper ore, copper sulfur ore, copper-molybdenum deposit, copper nickel, carrollite and so on. Basically, only flotation can be considered in its separation.
Almost all copper sulphide ores contain iron-bearing sulfides, so in a sense, the flotation of copper sulfide is essentially the separation of copper sulfide from iron sulfide. The common iron sulfide minerals in copper ore are pyrite and pyrrhotite.

Chalcopyrite: a kind of copper oxide ore
The main factors affecting the flotation of copper-bearing pyrite:
- Disseminated grain size and symbiotic relationship of copper and iron sulfide. Generally, pyrite has a coarse grain size, while copper ore, especially secondary copper sulfide, is closely associated with pyrite. Only when the copper ore is finely ground can it be dissociated from pyrite. This characteristic can be used to select copper-sulphur mixed concentrates, discard the tailings, and then grind and separate the mixed concentrate.
- The influence of secondary copper sulfide minerals. When the secondary copper sulfide mineral content is high, the copper ions in the slurry will increase, which will activate the pyrite and increase the difficulty of Cu-S separation.
- The influence of pyrrhotite. The high content of pyrrhotite will affect the flotation of copper sulfide. Pyrrhotite oxidation will consume the consumption of oxygen in the pulp. In severe cases, the copper minerals do not float at the beginning of flotation. This can be improved by increasing inflation.
There are three common flotation processes:
Preferential flotation
Generally, copper is floated firstly and then sulfur. The content of pyrite in dense massive copper-bearing pyrite is quite high and high alkalinity (free CaO content> 600~800g/m3) and high dosage of xanthine are often used to suppress the pyrite. There is mainly pyrite in its tailings with few gangues, so the tailings are sulfur concentrates.

Preferential flotation of copper sulfide ore beneficaition
For the disseminated copper-sulfur ore, the preferential flotation process is adopted, and the sulphur in the tailings must be re-floated. To reduce the consumption of sulfuric acid during the floatation and ensure safe operation, the process condition of low alkalinity should be adopted as far as possible.
Bulk-separating flotation
It is more advantageous for copper sulfur ore containing less sulfur with copper easy to be floated. Carry out the bulk flotation firstly in the weakly alkaline pulp and then add lime to the mixed concentrate to separate the copper and sulfur in the highly alkaline pulp.
Semi-preferential bulk-separation flotation
In semi-preferential bulk-separation flotation, Z-200, OSN-43 or ester-105 with good selectivity are used as collectors to float copper minerals firstly. The copper concentrate is then subjected to copper-sulfur bulk flotation and the obtained copper-sulfur mixed concentrate is subjected to separation flotation of floating copper and suppressing sulfur.

Semi-preferential bulk-separation flotation of copper sulfide ore beneficiation
It avoids the inhibition of the easily floating copper under high lime consumption and does not require a large amount of sulfuric acid-activated pyrite. It has the characteristics of reasonable structure, stable operation, a good index and early recovery of target minerals.
The floatability of copper sulfide minerals :
- All minerals that do not contain iron, such as chalcopyrite and covellite, have similar floatability and the inhibitory effect of cyanide and lime on them is weak.
- All iron-bearing copper minerals, such as chalcopyrite and porphyry, are easily inhibited by cyanide and lime in alkaline media.
- The xanthate collector mainly plays the role of chemisorption together with the cation Cu (2 +), so minerals whose surface contains more Cu (2 +) minerals have a strong effect with the xanthate. The order of the effect is: chalcocite > covellite > porphyrite> chalcopyrite.
- The floatability of copper sulfide minerals is also affected by factors such as crystal size, mosaic size, being original or secondary. The minerals with fine crystal and mosaic size are difficult to float. Secondary copper sulfide ore is easy to oxidize and more difficult to float than original copper ore.
As for the grinding and floating process, it is more advantageous to adopt the stage grinding and floating process for refractory copper ore, such as the re-grinding and re-separation of coarse concentrate, re-grinding and re-separation of bulk concentrate, and separate treatment of medium ore.
2. Beneficiation methods of copper oxide ore
Copper oxide (CuO) is insoluble in water, ethanol, soluble acid, ammonium chloride and potassium cyanide solutions. It can react with alkali when slowly dissolving in ammonia solution. The beneficiation methods of oxidized copper ore mainly include gravity separatio, magnetic separation (see details on copper ore processing plant), flotation and chemical beneficiation.
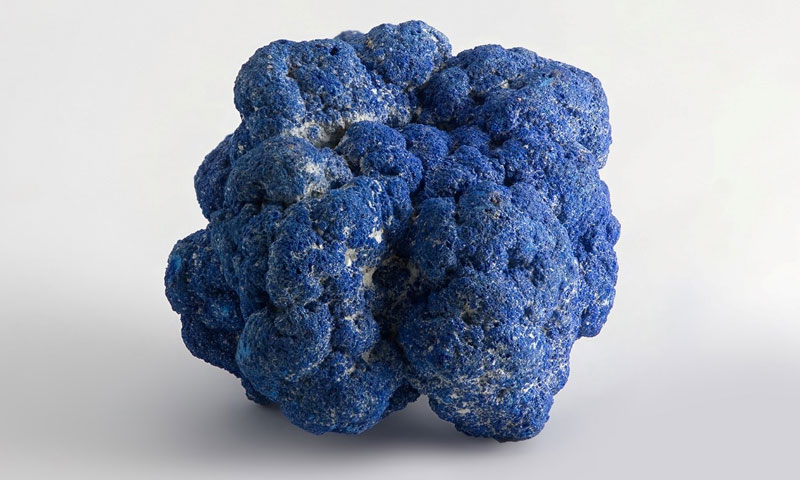

Azurite: a kind of copper oxide ore
Flotation method
Flotation is one of the commonly used mineral processing techniques for copper oxide ores. According to the different properties of copper oxide ores, there are sulphidizing flotation, fatty acid flotation, amine flotation, emulsion flotation and chelating agent-neutral oil flotation method.
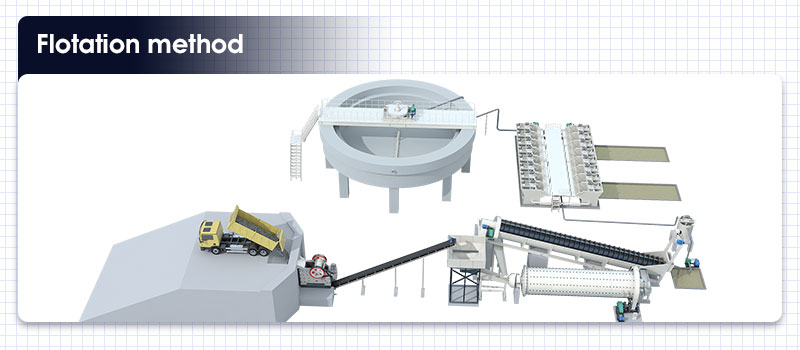
Flotation method of copper oxide ore
1. Sulphidizing flotation
The oxidized ore is vulcanized by adding vulcanizing agent and then the flotation is carried out with the ordinary reagents of copper sulphide flotation.
Scope of application: mainly malachite, azurite and atacamite.
Process flow: The dosage of sodium sulfide can reach 1~2kg/t during vulcanization. Because the film produced by vulcanization is not stable and is easy to fall off after vigorous stirring, and sodium sulfide itself is easily oxidized, sodium sulfide should be added in batches.
Besides, the vulcanization speed of malachite and azurite is relatively fast, so the vulcanizing agent can be directly added to the first flotation cell with no need to stir in advance during vulcanization and adjust the amount of vulcanizing agent according to the foam state.
Use of reagents:
- When there is much mud in the sludge: water glass must be added.
- Collector: butyl xanthine, or butyl xanthine mixed with aerofloat.
- The PH value of flotation pulp: around 9.
- Improve the flotation index: ammonium sulfate, sulfuric acid, etc.
2. Fatty acid flotation
Fatty acids and their soaps are mainly used as collectors of fatty acid floatation, also known as direct flotation. During flotation, water glass (gangue inhibitor), phosphate, and sodium carbonate (slurry regulator) are also usually added.
Scope of application: copper oxide mineral whose gangue is not carbonate.
There is a practice of mixing vulcanization and fatty acid methods. Firstly float the copper sulfide and part of the copper oxide with sodium sulfide and xanthate, and then float the residual copper oxide with fatty acid.
For example, the ore in the Nchanga processing plant in Zambia contains 4.7% copper. The copper content achieved to 50% ~ 55% through flotation by adding 500g/t of lime (pH 9 ~ 9.5), 10g/t of cresol (foaming agent), 60g/t of ethylxanthate, 35g/t of amyl xanthate, 1kg/t of sodium sulfide, 40g/t of palmitic acid and 75g/t of fuel oil.
3. Amine flotation
Amines are mainly used as collectors in this method. It can be used not only for the separation of copper oxide, but also for the beneficiation of copper oxide, lead, and zinc minerals.
Scope of application: malachite, azurite and chlorchlorite, etc.
The premise of amine flotation method is to firstly find effective inhibitors of gangue, such as seaweed powder, polyacrylic acid, etc.
4. Emulsion flotation
It is mainly to sulfurize the copper oxide mineral firstly and then add the copper accessory ingredient to create a stable oil-wet surface. Then, the neutral oil emulsion is used to cover the mineral surface, resulting in a strong hydrophobic floating state. In this way, the mineral can be attached to the foams firmly to complete the separation.
Emulsion flotation includes three aspects:
- 1 Use the selective copper accessory ingredients, including benzotriazole, mercaptobenzothiazole, diphenyl guanidine, etc.
- 2 Add non-polar oil emulsion to improve the adhesion of minerals and foams.
- 3 Use selective inhibitors such as acrylic polymers and sodium silicate.
5. Chelating agent-neutral oil flotation
It completes the flotation by using the mixture of the chelating agent and neutral oil as a collector.
Scope of application: refractory copper oxide (such as silicon malachite)
It not only has high selectivity and collecting effect, but also can guarantee high sorting index and reduce the consumption of reagents. Chelating agents also have selective inhibition effect.
However, the cost of chelating agents is relatively high. Currently, the chelating agents used include polyamine and condensation of organic halides, etc.
Problems should be noticed in the flotation of copper ore:
Many problems should be paid attention to in the flotation of copper ore, such as the length of the vulcanization time, whether to add sodium sulphide in batches and the proportion of chemicals. Here is a brief introduction.
- The vulcanization time. Different ores require different vulcanization times. Generally speaking, it should be short rather than longer. The suitable vulcanization time is 1 to 3 minutes. After 6 minutes, the recovery rate and concentrate grade will decrease.
- Add sodium sulfide in batches. The roughing time for processing the ore in the concentrator is about ten minutes, while the ore contains a large amount of carbonaceous gangue and the divalent sulfur ions disappear quickly in the slurry. So the effect of adding sodium sulfide in batches is better than that of adding it once.
- Add sodium sulfide proportionally. Generally, copper oxide floats in the liquid at a slower speed, and reduce the number of cycles of the mineral in the flotation process can obtain a higher recovery rate. It is of great significance to study the distribution ratio of sodium sulfide among different operations to catch the mineral at the right time.
Chemical beneficiation
The chemical beneficiation method is often used for refractory copper oxide and mixed copper. For some copper oxide minerals with high copper content, fine mosaic size and rich sludge, the chemical beneficiation method will be used to obtain good indicators because the flotation method is difficult to realize the separation.
It has many advantages such as simple process flow, low investment, low energy consumption, light pollution and low production cost.

Chemical beneficiation of copper oxide ore
Acid leaching—precipitation—flotation
Scope of application: malachite, cuprite, tenorite, copper mine tailings, etc., except copper ore containing calcium magnesium carbonate gangue.
The ore is first leached with a 0.5% to 3% sulfuric acid dilute solution after being ground. (For some ore that is difficult to be leached, it needs to be heated to 45 to 70° C during leaching).
The oxidation of copper mineral dissolves to generate copper sulphate that will be replaced with iron filings to restore copper ions to metallic copper for precipitation.
Finally, float the metallic copper and copper sulfide minerals insoluble in sulfuric acid to obtain copper concentrate.
Ammonia leaching
Scope of application: oxidized copper ore containing calcium and magnesium carbonate gangue minerals
The solution of ammonia and ammonium carbonate in a concentration of 12.5% was used as the solvent to leach for 2.5h at a temperature of 150℃, a pressure of 1925175~2026500Pa. The mother liquor can be distilled by steam at 90℃ to separate ammonia and carbon dioxide. Copper, on the other hand, is precipitated from the solution as black copper oxide powder.
Floatation - magnetic - metallurgy
Because some copper oxide minerals are not tightly combined with iron, manganese, etc., it is difficult to separate them by using the magnetic separation method alone, and flotation has a good separation effect.
Therefore, the flotation method is used to obtain high-grade concentrates, the magnetic separation is for tailings and wet smelting is carried out finally. This process combines flotation, magnetic and wet smelting very well, which greatly increases the recovery rate and reduces the beneficiation cost.
The above are several common beneficiation methods for copper oxide minerals. For the selection of copper oxide minerals, it is best to conduct a professional beneficiation test and customize the process according to the report.
Copper ore dressing equipment
1. Flotation machine
Flotation is the most widely used method in copper mine production. The copper ore pulp is stirred and aerated, and the ore particles adhere to the foams under the action of various flotation agents. The foams rise to form a mineralized foam layer, which is scraped or overflowed by the scraper. This series of flotation processes are all completed in the flotation machine. (Contact Manufacturer)

Flotation machine for copper ore dressing
Performance advantages of copper ore flotation machine
- The copper flotation machine increases the collision probability of coarse particles and foams, improves the mineralization effect of coarse particles, reduces the mismatch of materials and improves the recovery rate of concentrate.
- The copper mine flotation machine itself has good stability, so no special foundation is required for installation, saving manpower, energy and materials during installation.
2. Magnetic separator
Magnetic separator can recover useful magnetic minerals contained in copper ore. It can improve the taste of ore and the utilization rate of resources, and reduce the waste of resources.
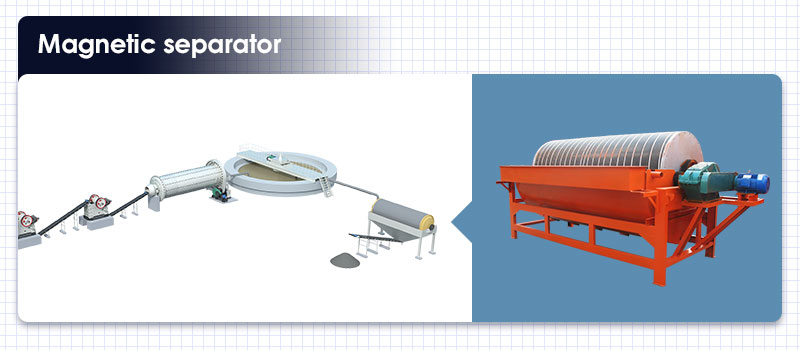
Magnetic separator for copper ore dressing
Performance advantages of magnetic separator:
(1) High technology
The internal magnetic system of the barrel adopts a short circuit design to ensure that the barrel skin has no magnetic resistance at high speeds, and the stainless-steel barrel skin does not generate high temperatures, extending the life of the magnetic block.
(2) High taste in the selection
Since it adopts a dynamic magnetic system design, the roller does not stick to the material, which is conducive to material sorting. The selected grade can be increased by 3-6 times to more than 65%.
3. Jigger
Copper mines are generally purified by flotation, but for the beneficiation of copper minerals with coarser grain size and higher density, the pre-selection by the gravity separation method will greatly reduce the cost and achieve flotation indicators.

Jigger for copper ore dressing
Performance advantage of jigger
- The jigger can be used to select both fine and coarse materials with the upper limit of its feeding grain size of 6-12 mm.
- Large processing capacity and wide selection range.
4. Shaking table
The shaking table is suitable for beneficiation of copper ore and can be used in different operation modes such as coarse separation, concentration and scavenging.
Shaking table for copper ore beneficiation
Performance advantages of shaking table
- Compared with the traditional process, the shaker has the advantages of no use of reagents, low energy consumption and easy management.
- Low investment cost.
Copper ore beneficiation plant
Below is a typical copper ore beneficiation plant in South Africa. It mainly uses the copper-lead bulk flotation separation method, which helps obtain copper and lead concrentrate.