Crushed stone is made by crushing large rocks and is widely used in construction, landscaping, agriculture, and other fields.
Stone crushing equipment can break down large rocks of different hardness into crushed stones suitable for different uses, maximizing the value of the material.
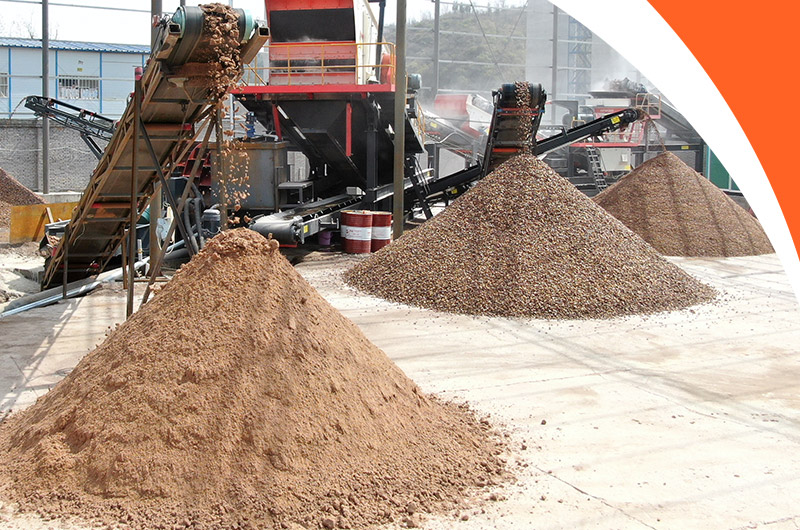

Many people may believe that breaking large rocks into small stones is a challenging task. In fact, with the assistance of modern high-efficiency stone crushers, this process is both simple and efficient.
Identifying stone types and hardness
The Mohs scale of hardness is widely used internationally to measure the hardness of stones and minerals. Hardness is a key factor in choosing the appropriate stone crusher, as different stones naturally have different hardness levels.
Hard stones, such as granite and basalt, usually require powerful jaw crushers and cone crushers for effective crushing.
The crushing process for some softer rocks is simpler, as they require less crushing force.
Here are the most commonly used types of rocks for producing crushed stone and their Mohs hardness:
| Common Rocks | Mohs Hardness | Characteristics |
| Granite | 6–7 | Durable, used for construction, needs strong crushing force |
| Quartzite | 7 | Very hard, used in high-wear environments |
| Basalt | 6 | High hardness, used in construction and paving |
| Sandstone | 2–7 | Hardness depends on the proportion of its mineral components, used in construction and decoration |
| Limestone | 3–4 | Relatively soft, easy to crush, used in construction and cement manufacturing |
| Marble | 3–4 | Easy to work with, used for decoration and sculpture |
| Gypsum | 2 | Very soft, used in drywall and cement additives |
| Talc | 1 | Softest mineral, used for talcum powder, easily crushed by hand |
Which equipment can be used for crushing rocks?
The key to obtaining high-quality crushed stone is choosing a stone crusher that matches the material characteristics.
With extensive industry experience and a deep understanding of the performance of various stone crushers, FTM Machinery offers the following recommendations:
1. Gyratory Crusher Get a Quote
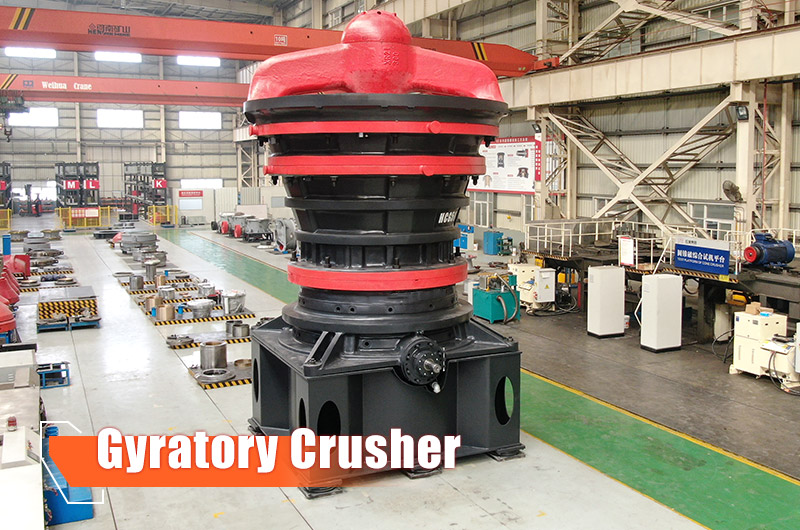

- Parameters: Maximum feed size 1,350 mm, production capacity 2,354–14,082 t/h
- Features: Gyratory crushers are suitable for the primary crushing of medium to high hardness and abrasive rocks like granite and basalt. Not suitable for sticky materials. Typically used in medium to large stone processing projects for high output.
- Output: Coarse aggregates
2. Jaw Crusher Get a Quote

- Parameters: Maximum feed size 1,200 mm, production capacity 105–1,590 t/h
- Features: Jaw crushers are typically the primary choice for hard rock crushing, capable of handling high humidity and high viscosity rocks. They are the best choice for medium to small-scale stone production lines.
- Output: Coarse aggregates
3. Cone Crusher Get a Quote

- Parameters: Maximum feed size 450 mm, production capacity 85–2,181 t/h
- Features: Cone crushers are suitable for secondary or even tertiary crushing of medium-hard rocks. They cannot crush wet or sticky stones. Cone crushers produce well-shaped crushed stone and are ideal for large quarry operations.
- Output: Medium to fine aggregates
4. Impact Crusher Get a Quote

- Parameters: Maximum feed size 800 mm, production capacity 60–2,000 t/h
- Features: Impact crushers are suitable for secondary and tertiary crushing of medium-hard, brittle, and low-abrasive stones like limestone and shale. They occupy a small footprint and are easy to maintain.
- Output: Medium to fine aggregates, producing cubic-shaped stones with minimal fines.
5. Hammer Crusher Get a Quote
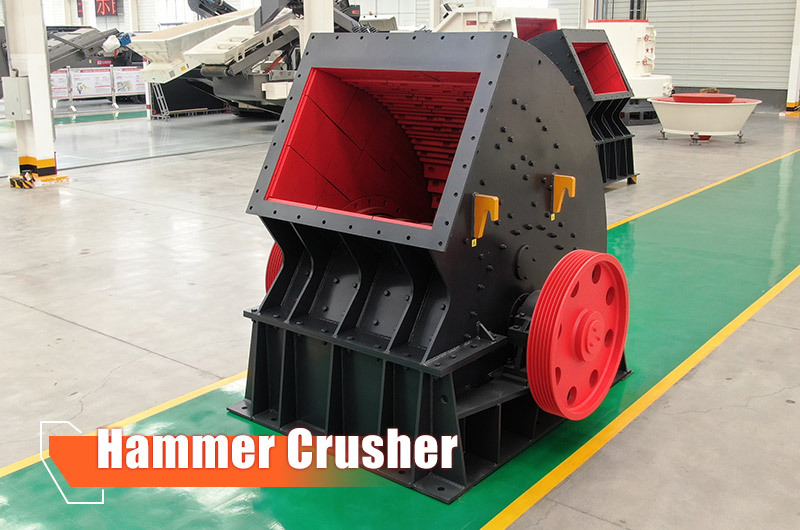
- Parameters: Maximum feed size 300 mm, production capacity 3–95 t/h
- Features: Hammer crushers are suitable for medium to fine crushing of medium-hard and brittle materials achieving a high reduction ratio of up to 50 with finer output (≤40 mm). They are ideal for small-scale production. Heavy hammer crushers are ideal for secondary crushing and shaping in large-scale, high-output production lines.
- Output: Hammer crushers produce medium to fine aggregates, while heavy hammer crushers produce coarse aggregates.
6. Roll Crusher Get a Quote

- Parameters: Maximum feed size 30 mm, production capacity 3–110 t/h
- Features: Roll crushers are suitable for medium to fine crushing and sand making of hard and brittle rocks. They can crush materials like coal, clay, or stones with high moisture content.
- Output: Fine aggregates with uniform particle size distribution and low oversize material.
7. Sand Making Machine / Vertical Shaft Impact Crusher Get a Quote
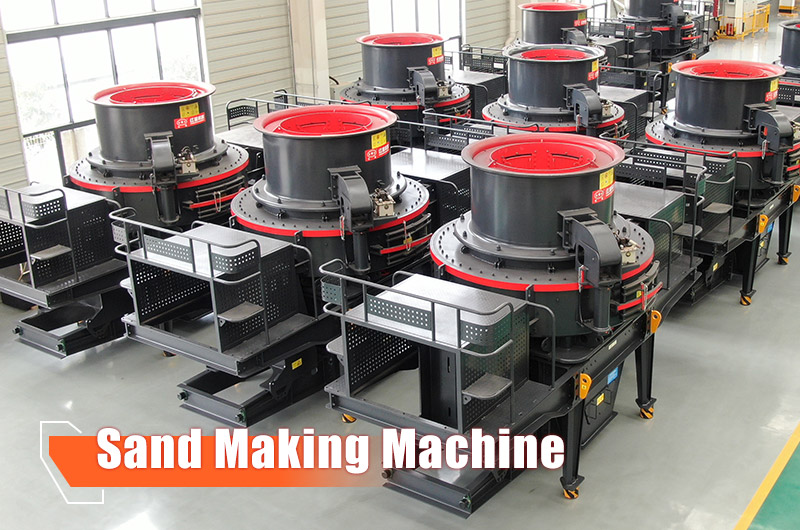

- Parameters: Feed size <45 mm for hard materials, <50 mm for soft materials, production capacity 80–650 t/h
- Features: Sand making machines are tertiary crushers that crush rocks into gravel, characterized by fine crushing and coarse grinding, producing high-quality sand products.
- Output: Fine sand
Crucial equipment after crushing: rock screeners Get a Quote
Following rock crushers, rock screeners become crucial as they precisely classify crushed stone into large, medium, small stones, and stone powder, meeting specific granularity requirements for various engineering projects.
There are various types of vibrating screeners, including circular and linear screens. These machines can feature single or multiple layers of screens to accurately separate materials by size.

- Circular vibrating screen: Utilizes circular motion to move materials across the screen, suitable for sticky or wet materials, commonly used in stone crushing, sand production, and ore processing.
- Linear vibrating screen: Moves materials in a straight line, offering higher screening efficiency, ideal for fine screening and classification of diverse materials.
What is crushed stone used for?
Crushed stone is widely used across multiple industries including construction, agriculture, forestry, and landscaping due to its durability and aesthetic appeal, demonstrating versatile utility.

- Road construction: Used as a base layer for roads and highways, providing a stable foundation to distribute weight and support road surfaces.
- Foundations for concrete and pavers: Essential aggregate in producing concrete and asphalt. Additionally, used as a base for concrete and pavement bricks to enhance stability and facilitate drainage.
- Drainage control: Commonly employed in drainage systems such as French drains, facilitating effective water flow away from buildings and flood-prone areas.
- Soil improvement: In agriculture, crushed stone enhances soil drainage and aeration, promoting healthier plant growth.
- Landscaping: Various colors and sizes of crushed stone are used to create pathways, walkways, or decorative ground cover in gardens and parks, offering aesthetic appeal and visual interest.