In the construction industry, manufactured sand (M sand) is widely used in the production of concrete and mortar mix due to its stable quality and controllable particle size distribution.
Compared with natural river sand, M sand can be produced through an artificially controlled sand making process to meet specific civil engineering needs.
In order to produce high-quality machine-made sand, you must first understand its characteristics. Therefore, this blog will explore some key factors that affect the quality of sand on this basis, helping you adjust the sand production line accordingly.
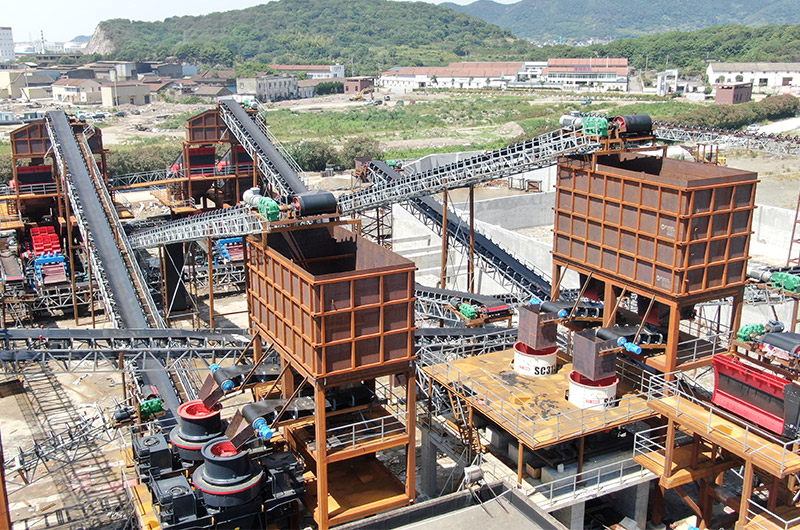

About Manufactured sand
Manufactured sand, the full form of M sand, is also called artificial sand or crushed sand. It is manufactured by crushing large rocks, stones, or ores into fine particles, which are then washed and finely graded.
However, natural sand is formed by natural processes. It comes from rivers, lakes and oceans, and contains human, and animal bones, and its strength and durability depend on natural conditions.
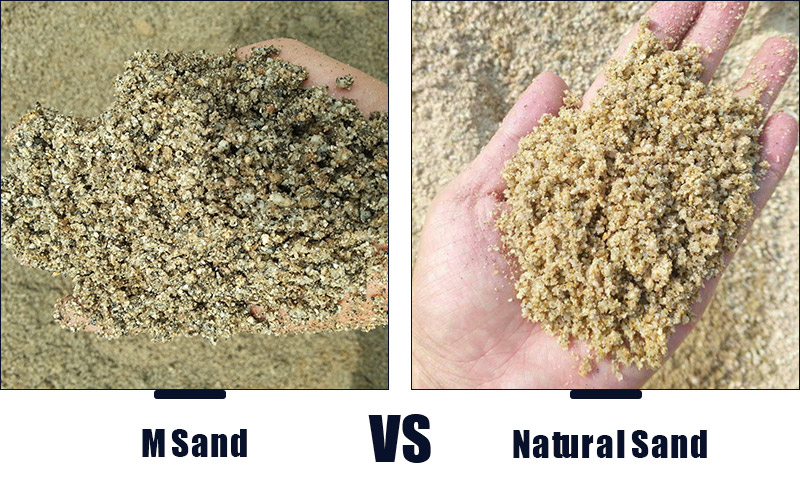

Except for the different sources, the M sand manufacturing process has less impact on the environment. It will not damage riverbeds and erode coasts and is more sustainable than mining natural sand.
In terms of uses, M sand (such as silica sand and quartz sand) is widely used in the production of building materials such as concrete, mortar, and asphalt, while natural sand is commonly found in construction, casting, and glass manufacturing.
In terms of performance, M sand has obvious performance advantages:- Precise particle size control, higher fineness modulus than natural sand
- Rough texture and high stone powder content boost concrete fluidity, increasing compressive strength by 6%–9% and flexural strength by 12%–15%
- Fewer impurities (such as clay, dust, and silt) and denser particle packing improve wear resistance in concrete
- Cubic or angular particles enhance cement bonding strength
- Local production near construction sites can reduce transportation costs by 30%–50%
- M sand for concreting—used in concrete
- M sand for plasterin—used in tiling and wall plastering purposes
- M sand for brick or blockwork—used for masonry or brick or block-laying works
Six factors affecting the quality of M sand
1. Raw material selection
When selecting raw materials, we need to consider the composition of the parent rock, raw material strength, mud content, and powder content. By rationally selecting and pre-treating raw materials, the quality of M sand can be effectively improved.
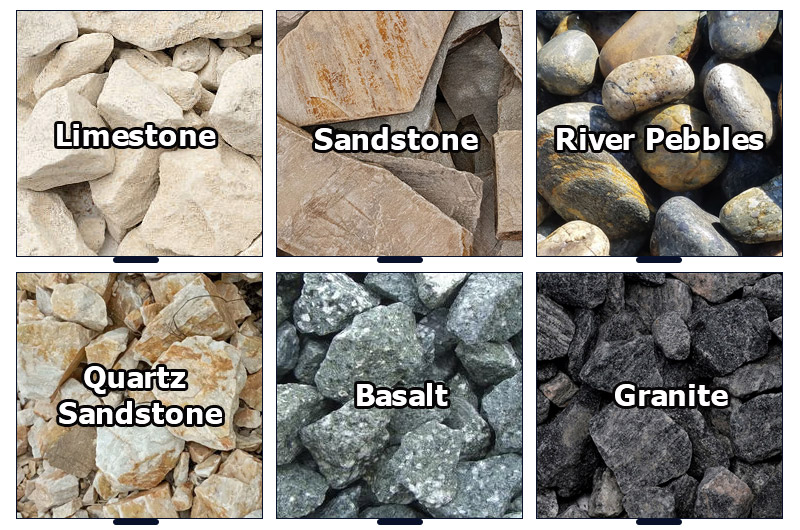

The chemical and mineral composition of the parent rock determines if artificial sand contains harmful substances and alkali-aggregate reactivity. The parent rock must not have potential alkali-aggregate reactivity.
Raw material strengthRaw materials for artificial sand must have high compressive strength of at least 150 MPa. Granite, basalt, and river pebbles are commonly recommended.
Mud content
It is very important to control the mud content in the raw material. The proportion of mud should be minimized when mining.
Powder content
Too high powder content will affect the material transportation and reduce the output of the sand making machine. By pre-screening and removing excessive fine powder, the impact on the operation of the sand making machine can be reduced.
The following are some of the best raw materials for sand making:- Quartz sandstone: Its strength and particle shape reach or even exceed natural sand.
- River pebbles: Pebble sand is the best choice to replace natural sand in terms of strength, particle shape, and color.
- Limestone: It can be used as a sand and gravel raw material on the sand and gravel production line at the same time, and the stone powder can also be reused.
- Basalt: Mixing sand made from basalt into concrete makes the concrete lighter but still very strong. It also has the characteristics of sound insulation and heat insulation.
- Granite: Granite with high quartz content and low sulfide content is a high-quality sand making raw material, but the pulverization problem must be solved.
2. Sand crushing process
Different materials require different crushers to reduce the particle size. We use primary crushers, secondary crushers, and tertiary crushers for coarse crushing, medium crushing, and fine crushing of materials.
① Primary crusher
Using a jaw crusher to initially crush large rocks is a crucial step because it determines the efficiency of subsequent crushing and the quality of the final product.

Advantages: High crushing capacity, adjustable output size, energy saving, durable
Maximum feed size: ≤1,200 mm
Output size: 10–350 mm
Capacity: 1–1,435 tons/hou
② Secondary and tertiary crushers
Secondary crushing usually uses an impact or cone crusher to further reduce the particle size of the material in preparation for fine crushing in the sand making machine.

Advantages of impact crusher machine: High crushing efficiency, large output, good and uniform product grain shape, low failure rate, low power consumption
Feed size: ≤800 mm
Capacity: 30–2,000 t/h

Model of cone crushers: Single cylinder, multi-cylinder, fully hydraulic cone crusher
Advantages: Suitable for hard rock processing, large capacity, high crushing efficiency
Feed size: ≤480 mm
Capacity: ≤2,181 t/h
3. Sand making process
The sand making machine is the core equipment for manufacturing sand. Through the high-speed rotating rotor and throwing disc, the material collides and rubs multiple times in the crushing chamber to form sand of the required particle size.

Our best-selling M sand making machine: VSI sand maker, HVI sand maker
Advantages: They have the best sand making effect and can be designed as mobile models
Maximum feed size: hard materials <50 mm, soft materials <55 mm
Capacity: 50–703 t/h
If you are not so strict about machine-made sand, you can also use hammer crushers, double roller crushers, and compound crushers to produce sand. Want to know more about sand making equipment?
4. Sand screening and grading
Screening is a key step to ensure uniform distribution of M sand size. Using a vibrating screen to grade sand can ensure the separation of sand and gravel of different particle sizes, remove dust particles, and meet the needs of different projects.

High screening efficiency, 6.0G vibration intensity
Screen materials: High manganese steel woven screen, punched screen plate, rubber screen plate, etc., with 1–4 layers and sizes of 1–140 mm
Screening particle size: Coarse sand (above 0.5 mm), medium sand (0.35–0.5 mm), fine sand (0.25–0.35 mm)
5. Sand washing and drying
Washing sand can improve the purity of the sand. One wash can remove particles of 0–150 microns and other impurities. Sand drying ensures that the sand in dryer will not be affected by excessive moisture during storage and transportation.

Sand washing equipment types: Wheel and spiral type sand washer
Wheel sand washing machine: The capacity is 15–300 t/h. The feed particle size is within 10 mm. Less fine sand loss.
Spiral sand washer: The capacity is 5–240 t/h. The feed size is within 10 mm. It has a cleaner washing effect.

Using a sand dryer can pbtain high-quality final product, making the material moisture is dried to within 0.5–1%
Short drying time, zero dust pollution, zero noise
30% energy saving, 20% reduction in power consumption
6. Quality Control
Improving the grade of sand requires establishing a strict quality control process, including regular testing of sand particle size, grading, mud content, and other indicators to ensure that the machine-made sand meets national or industry standards.
Standards for the grade of sand:- Fineness Modulus: It is an indicator of the coarseness of machine-made sand, usually between 2.3 and 3.2. The smaller the fineness modulus, the finer the sand; the larger the fineness modulus, the coarser the sand. This indicator affects the fluidity and strength of concrete.
- Particle Size Distribution: It refers to the ratio of particles of different sizes in sand. Good grading can improve the density and strength of concrete and reduce the amount of cement.
- Mud Content: It refers to the content of particles smaller than 0.075mm in machine-made sand. High mud content will reduce the workability and strength of concrete and increase the risk of shrinkage and cracking of concrete.
- Stone Powder Content: It refers to the content of particles smaller than 0.15mm in machine-made sand. An appropriate amount of stone powder can improve the fluidity of concrete, but excessive stone powder will reduce the strength of concrete.
- Mica Content: Too high a mica content may affect the frost resistance of concrete.

These standards ensure that the quality of M sand meets the requirements of the construction industry, thereby ensuring the performance and life of concrete and other building materials.
Conclusion
Optimization of the sand crusher machine and sand manufacturing process is the key to manufacturing high-quality civil engineering sand. FTM Machinery sand making plants will be more automated and intelligent to provide the construction industry with more efficient and environmentally friendly sand and gravel aggregates.