What is a ball mill?
A ball mill, also known as a ball mill machine, is a grinder that reduces the size of materials by using a rotating cylinder filled with grinding media such as steel balls or ceramic balls.
Ball mills are primarily used for crushing and grinding materials. They can handle feed from a jaw crusher in the primary grinding stage or feed from other grinding equipment, like a rod mill or SAG mill, in the secondary grinding stage.
Ball mill applications
Ball mills are commonly used in industries such as mineral processing, cement production, chemicals, ceramics, and fertilizers to crush and grind various materials such as ore, limestone, quartz, coal, etc.

1. Mining and mineral processing
Ball mills are widely used in the grinding process of various metal ores, including gold ore, copper ore, iron ore, silver ore, zinc ore, tungsten ore, and lead ore. By reducing ore particle size, valuable minerals can be extracted more effectively.
Additionally, ball mills are used to grind materials like bentonite, kaolin, barite, and talc. In ore processing, ball mills typically work alongside crushers, flotation machines, magnetic separators, and gravity separators.
2. Cement grinding
Cement ball mills are mainly used to grind clinker and gypsum into fine powder for cement production. They can also be used to grind materials like slag, pozzolana, dolomite, and fly ash, which are added to cement to improve its strength and durability.
3. Fertilizer production
In fertilizer production, ball mills are used to grind raw materials like phosphate rock and limestone into fine powder, and to effectively mix materials like urea and ammonium nitrate, enhancing the quality of the fertilizer product.
Ball mills are also widely used for grinding coal, coke, construction materials, glass, silica sand, marble, and other materials.
4. Ceramics production
In the ceramics industry, ball mills are used to grind ceramic raw materials, such as feldspar, quartz, and clay. The finely ground materials can form a more uniform slurry, leading to ceramic products that are more consistent and durable.
In addition to grinding, ball mills are also used for mixing, stirring, and dispersing materials. They are popular in industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
To meet different production needs, FTM Machinery offers a variety of ball mill models with various specifications:
| Model | Ball load(t) | Feeding size(mm) | Discharging size(mm) | Capacity(t/h) | Motor power(kw) | Total weight(t) |
| Ф900×3000 | 2.7 | <20 | 0.075-0.89 | 1.1-3.5 | 22 | 6.98 |
| Ф1200×4500 | 5 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 1.6-5.8 | 55 | 15.6 |
| Ф1500×5700 | 12 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 3.5-6 | 130 | 25.8 |
| Ф1830×4500 | 15 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 4.5-12 | 155 | 38 |
| Ф2100×3000 | 15 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 6.5-36 | 155 | 45 |
| Ф2200×7000 | 35 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 15-28 | 380 | 62.5 |
| Ф2400×4500 | 30 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 8.5-60 | 320 | 72 |
| Ф2700×4500 | 48 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 26-90 | 480 | 102 |
| Ф3600×6000 | 110 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | As per process conditions | 1250 | 198 |
| Ф4000×5000 | 121 | <25 | 0.074-0.4 | 45-208 | 1500 | 230 |
For more options and custom solutions, please contact our expert team for detailed support and consultation. Inquire now!
Ball mill types
Ball mills come in various types based on applications and process requirements. Below are the types classified by process conditions, structural form, grinding media, and length-to-diameter ratio of the drum.
1. By process conditions
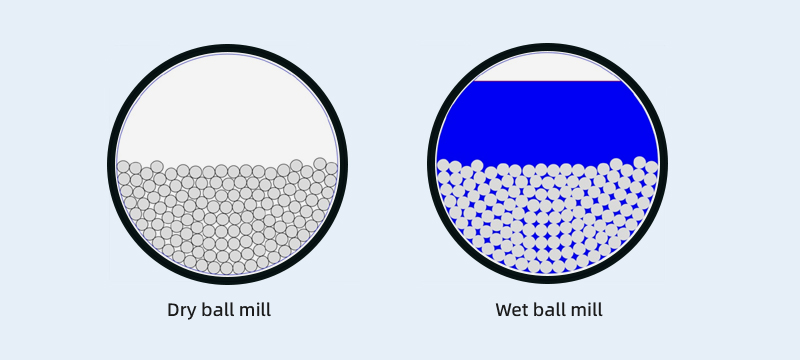
- Dry ball mill: Grind the material into mineral powder with the required fineness. Dry ball mills are suitable for hard materials like silica sand, quartz, marble, and cement clinker.
- Wet ball mill: Grinds materials into a slurry with a specific concentration, typically 60%–70%. Wet ball mills are commonly used in mineral processing and usually have a single-chamber structure.
Difference: The key difference between dry ball milling and wet ball milling is whether water is added during the grinding process. Adding water means wet type.
2. By structural form
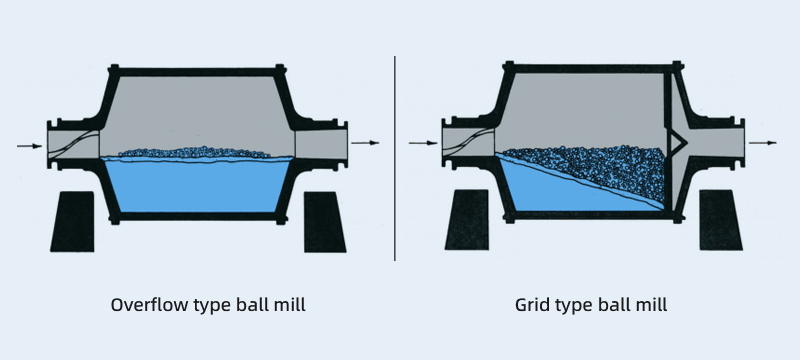
- Overflow type ball mill: Produces finer grinding results and is suitable for the second stage in a two-stage grinding process. The feed size is generally less than 0.2 mm. Its output is about 15% lower than that of a grid type ball mill of the same size, and it also uses less grinding media.
- Grid type ball mill: Suitable for situations where the product particle size is 0.2 mm–0.3 mm and needs to be uniform. This type of mill quickly discharges qualified products, reduces over-grinding, and increases grinding efficiency. It is often used in the first grinding stage.
3. By grinding media
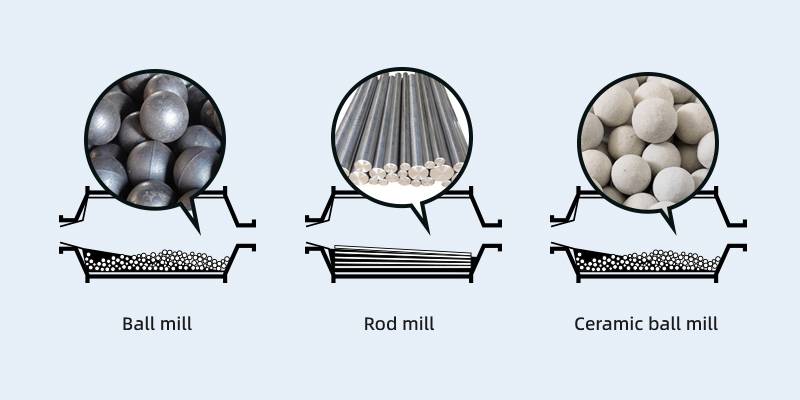
- Ball mill: Uses cast grinding steel balls and forged grinding steel balls as the grinding media.
- Rod mill: Uses grinding rods and grinding cylpebs as the grinding media.
- Ceramic ball mill: Uses ceramic balls as the grinding media.
4. By length-to-diameter ratio of the drum
- Ball mill: A typical ball mill has a drum length that is equal to or 1.5 times the drum diameter.
- Tube mill: A mill with a drum length-to-diameter ratio greater than 1.5 is referred to as a tube mill.
Ball mill main parts
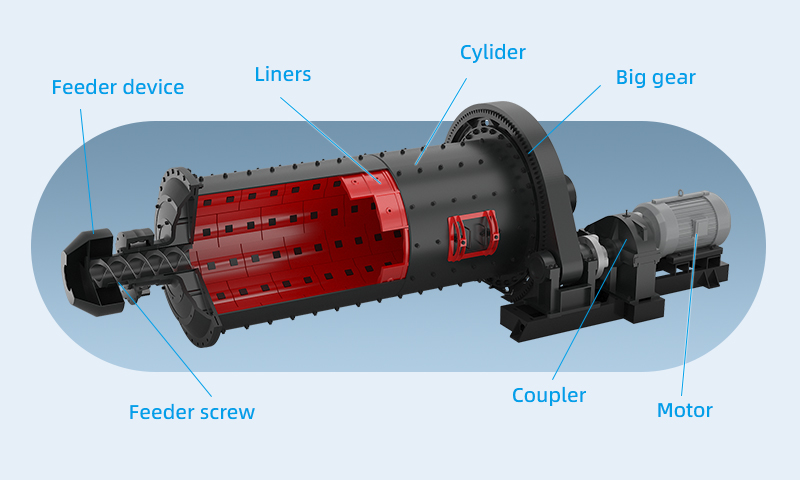
A ball mill primarily consists of several important parts: the cylinder, grinding media, drive system, feed and discharge ports, bearings, and liners.
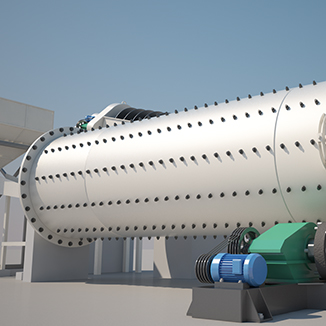
1. Cylinder
The cylinder is the main working part of the ball mill, where the grinding process occurs. It is a cylindrical structure usually made of steel plates. The interior of the cylinder is lined with liners to protect its inner walls.

2. Grinding media
Grinding media, typically steel balls or ceramic balls, is used to grind the material. The type and size of these balls affect grinding efficiency. Choosing the appropriate ball type, size, and ratio of large, medium, and small balls should be based on the material being ground.
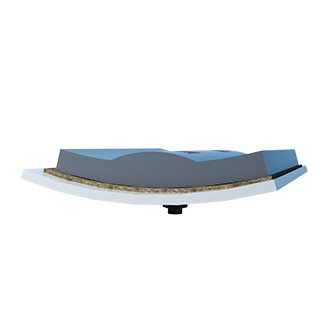
3. Liners
Liners are installed inside the cylinder to protect it from wear and to help the grinding media move. They can be made from materials like alumina ceramics, high-manganese steel, rubber, quartz, SILEX, or special materials. For grinding hard minerals, iron-free designs are often used.
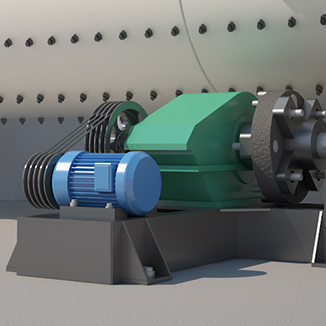
4. Drive system
The drive system powers the ball mill, including the motor, gearbox, gears, and essential control systems. The motor drives the large gear through a reducer, causing the cylinder to rotate and, in turn, driving the grinding media and materials inside the mill.
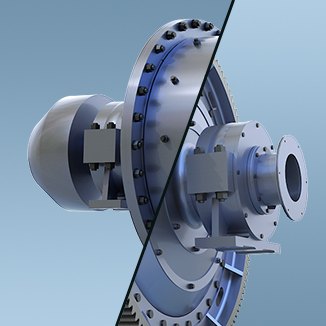
5. Feed and discharge ports
The feed port is at one end of the cylinder and is equipped with a feed screw to increase the feed volume. The discharge port at the other end releases the ground material, often equipped with a grate or overflow device to control particle size.
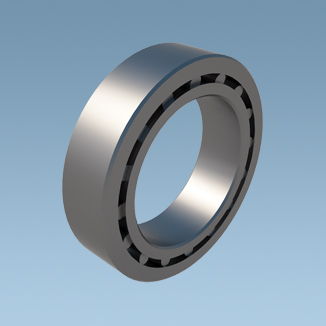
6. Bearings
Bearings support the rotating cylinder. Rolling bearings are used instead of traditional sliding bearings, reducing energy consumption by 15%–20%. Small ball mills use anti-friction cylindrical roller bearings, while large ball mills use trunnion and hydrostatic bearings.
Ball mill working principle
The ball mill operates based on impact and abrasion effects.
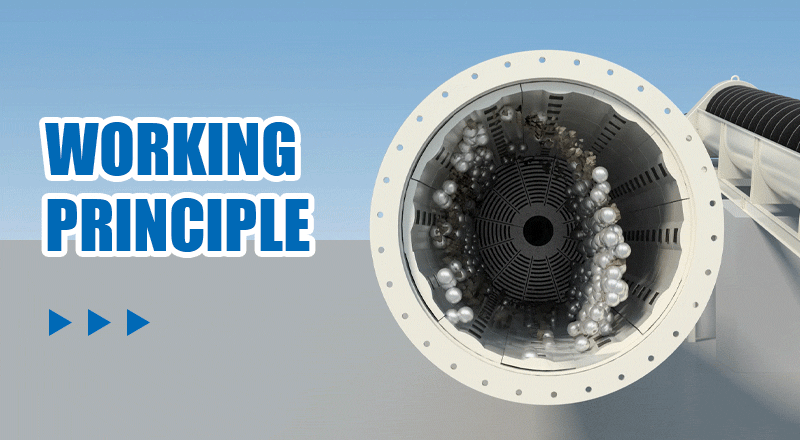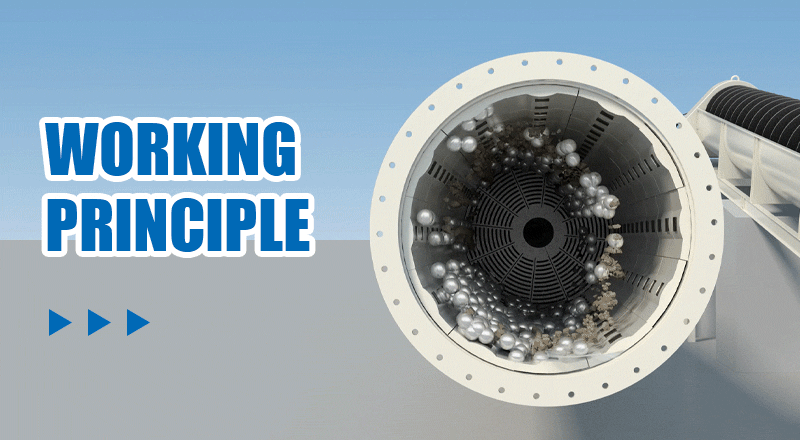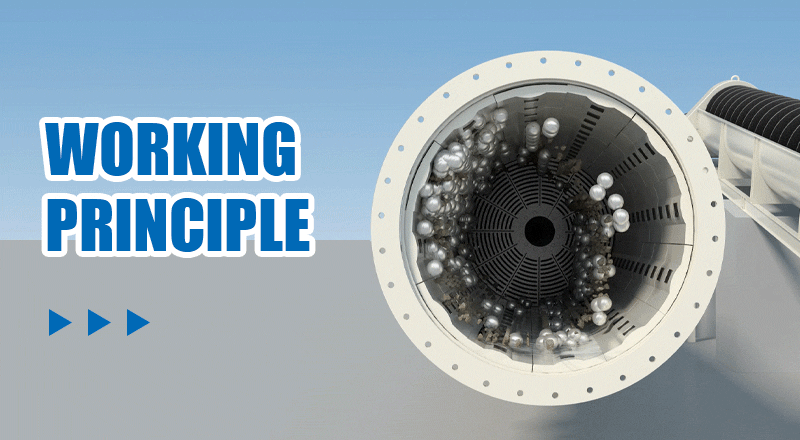
Step 1Loading: First, the material to be ground and grinding media (such as steel balls or ceramic balls) are loaded into the ball mill cylinder. Typically, the grinding media fills 30% to 45% of the cylinder's volume.
Step 2Rotational motion: When the ball mill starts, the motor drives the cylinder to rotate. As the cylinder turns, the grinding media are lifted to a certain height by centrifugal force.
Step 3Impact: Once the grinding media reach a certain height, gravity causes them to fall, generating a strong impact force on the material. This force breaks or crushes the material.
Step 4Abrasion: In addition to impact, friction between the grinding media and between the media and the cylinder walls further refines the material through abrasion.
Step 5Discharge: After repeated impact and abrasion, the material is ground to the desired fineness and is discharged through the outlet.
Why FTM Machinery ball mills?
FTM Machinery is dedicated to providing efficient and reliable solutions. With over 40 years of ball mill technology experience, we produce durable and robust ball mills that deliver higher value at lower costs.
- High production capacity: Capable of continuous operation with a maximum capacity of up to 615 t/h, meeting large-scale production needs.
- Energy efficiency: Rolling bearings replace traditional sliding bearings, reducing energy consumption by 15%–20%.
- Durable parts: Liners and discharge grates use advanced casting and heat treatment techniques to minimize wear during operation.
- Flexible design: Choose between grid or overflow discharge ports, and a spiral forced feed device for increased feed capacity. Optional iron separators are available.
- Dry oil lubrication system: Large and small gears use dry oil spray lubrication, offering high efficiency, low oil consumption, compact design, and no oil leakage.
- Eco-friendly: The ball mill and classifier form a closed system with negative pressure conveying, reducing dust and making it suitable for handling toxic substances.
- Quality service: FTM Machinery offers ample parts supply, including large and small gears, steel balls, and bearings, minimizing maintenance and replacement time.
Customer case—Ball mill for sale in Zambia
A copper mining company in Zambia introduced FTM Machinery's Ф2700×4500 ball mill to enhance the processing efficiency of copper ore.
Based on their production requirements, FTM Machinery recommended this ball mill to ensure efficient grinding and consistent high-quality output. Here are the project details:
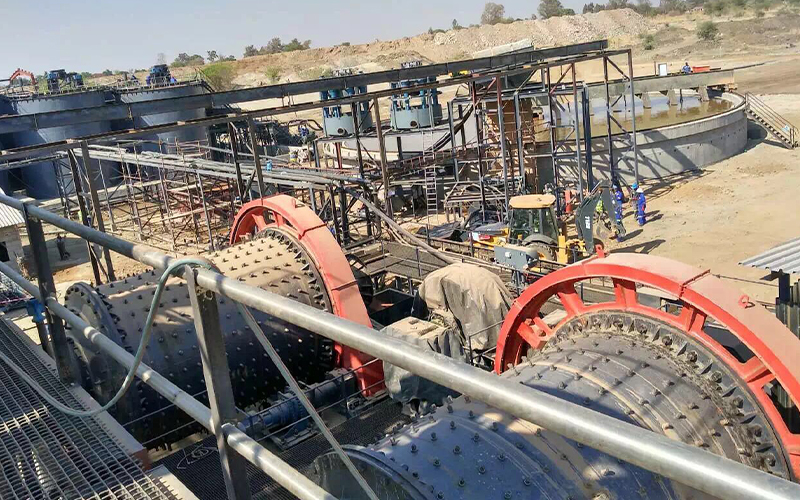

| Raw material | Copper ore |
| Hardness | Medium |
| Equipment model | Ф2700×4500 ball mill |
| Capacity | 60 t/h |
| Feed size | ≤25 mm |
| Discharge size | 0.074–0.4 mm |
FTM Machinery's ball mills have gained widespread market acclaim for their exceptional quality and are exported to numerous countries and regions, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Russia, the Philippines, and Vietnam. We will arrange prompt delivery as long as your country has trade licensing.
Here are the fastest shipping methods and approximate delivery times for some customer countries/regions:
| Location | Country | City | Delivery method | Time required(days) |
| Southeast Asia | Indonesia | Jakarta | Shipping | 11 |
| Malaysia | Klang | Shipping | 12 | |
| Philippines | Manila | Shipping | 5 | |
| Middle Asia | Uzebikistan | Tashkent | Railway | 16 |
| Kazakhstan | Almaty | Railway | 8 | |
| West Asia | Saudi Arabia | Jeddah | Railway | 25 |
| South Asia | Pakistan | Karachi | Shipping | 26 |
| Africa | South Africa | Durban | Shipping | 30 |
| Zambia | Lusaka | Shipping | 45 | |
| Kenya | Mombasa | Shipping | 32 | |
| Egypt | Alexander | Shipping | 34 | |
| Nigeria | Lagos | Shipping | 45 | |
| Europe | Russia | Vladivostok | Shipping | 10 |
| UK | Felixstowe | Shipping | 35 | |
| North America | The USA | Los Angeles | Shipping | 20 |
| Canada | Vancouver | Shipping | 22 | |
| Mexico | Manzanillo | Shipping | 21 | |
| South America | Brazil | Santos | Shipping | 35 |
| Argentina | Buenos Aires | Shipping | 35 | |
| Oceania | Australia | Sydney | Shipping | 20 |
| Papua New Guinea | Port Moresby | Shipping | 30 |

 Download Ball Mill
844.75 KB
Download Ball Mill
844.75 KB


