In nature, gold does not react with oxygen to form oxides like iron or copper does. Whether buried in tombs, sand, or resting on the seabed for thousands of years, gold nuggets, grains, and bars continue to shine brightly.
So, if gold does not oxidize, what exactly is oxidized gold ore?
Understanding Oxidized Gold Ores
Oxidized gold ore refers to gold-bearing ore formed through natural oxidation processes, rather than gold oxides.
Such ores typically contain gold along with oxides of metals like iron, copper, and manganese. The main minerals are limonite and pyrite, with little or no sulfides, but they do include stable secondary minerals like gold-bearing iron hydroxides or hydrated iron oxides, along with some quartz.

Surface weathering transforms primary sulfide minerals into oxides and hydroxides, with gold potentially being embedded in hematite, goethite, or limonite.
Oxidized gold ore usually appears yellow to brown and has a loose texture. It is an important raw material for gold production.
How to extract gold from oxidized gold ore?
In oxidized gold ore, most of the gold is contained within the main gangue minerals and the cracks of weathered metal oxides. The gold particle size varies greatly, and the mineral composition is relatively simple.
Before starting crushing and grinding processes, pre-treating the gold ore with a trommel screen is a crucial step for improving beneficiation efficiency, especially for oxidized gold ores containing clay.
Subsequently, gold extraction can be performed using methods such as gravity separation, cyanidation, or heap leaching.
Step 1: Ore crushing
Crushing reduces the size of oxidized gold ore and is usually done using a dry process with two to three consecutive crushing stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
For primary crushing of hard rock, a jaw crusher is used. It crushes the oxidized gold ore by compressing it between a fixed and a moving wear-resistant jaw plate, though the resulting product is often coarse and slabby.
Secondary and tertiary crushing use cone crusher, which is regarded as the best helper for crushing ores above medium hardness. It reduces the material by compressing it between the moving and the fixed steel plate, providing a more uniform fine particle size than the primary stage.


After crushing, a vibrating screen is used to classify the oxidized gold ore. Smaller particles pass through the screen openings while larger particles remain on the screen surface and are returned for further crushing.
Step 2: Ore grinding
Grinding releases the gold from the gangue minerals in oxidized gold ore, creating favorable conditions for subsequent beneficiation. Common grinding equipment includes ball mills and wet pan mills.

Ball mills have been the primary piece of machinery in traditional hard rock grinding circuits for 100 years. Use of a ball mill is the best choice when long term, stationary milling is required, especially when handling large volumes of oxidized ore.
Compared to ball mills, wet pan mills are more suitable for small to medium-sized oxidized gold ore beneficiation plants. They cost much less and are easier to maintain, making them a great alternative to ball mills. Although wet pan mills have a lower output, they provide a uniform grinding effect.
| Equipment | Feed size | Discharge size | Capacity | Cost |
| Ball Mill | <25 mm | 0.074–0.89 mm | 0.65–615 t/h | High |
| Wet Pan Mill | ≤30 mm | 0.074–0.6 mm | 1–50 t/h | Low |
Step 3: Ore beneficiation
Oxidized gold ore beneficiation is a complex and critical process. Different extraction processes can be selected according to the nature of the ore and the form of gold. The following are several common beneficiation methods:
1. Gravity separation
Gravity separation is a physical method that uses the difference in specific gravity between gold ore and gangue minerals for separation.
Commonly used oxidized gold ore gravity separation equipment includes shaking table, spiral chute, jig, etc.

| Equipment | Applicable particle size | Capacity |
| Shaking Table | Coarse sand (0.5–2 mm), fine sand (0.074–0.5 mm), sludge (≤0.074 mm) | 10–60 t/d |
| Spiral Chute | Fine minerals (0.02–0.3 mm) | 2–40 t/h |
| Jig | Coarse minerals (typically >2 mm) | 30–250 t/h |
- Shaking Table: It has a low processing capacity but is suitable for small to medium-sized dressing plants requiring high sorting accuracy. It handles fine gold ore and is simple to operate with low cost.
- Spiral Concentrator: Ideal for large-scale operations, it has a high processing capacity, efficiently handling medium to fine gold ore with continuous, stable performance.
- Jig: Used for coarse gold ore separation. It has high processing capacity and is suitable for large-scale initial separation or roughing.
2. Cyanidation
Cyanidation method is the most widely used chemical method for gold extraction. It is suitable for small and medium-scale mining of oxidized gold ores, especially those with fine particle size and high grade.
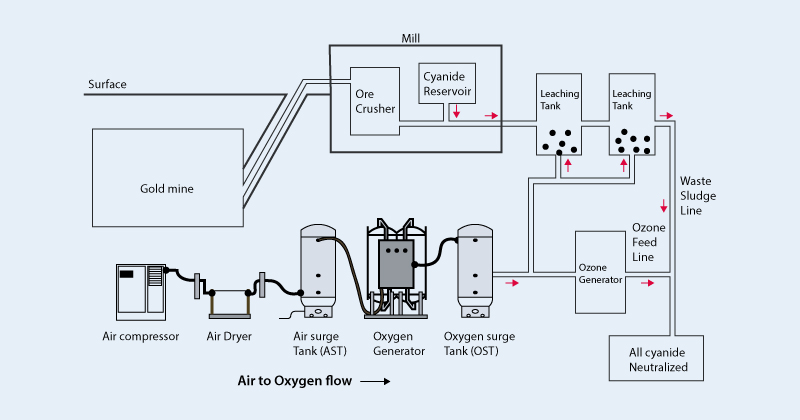
After grinding, the oxidized gold ore is mixed with cyanide solution, and the gold is dissolved in the liquid through leaching reaction, and then the gold is recovered by activated carbon adsorption or zinc precipitation.
Cyanidation offers high gold recovery rates and wide applicability but involves complex operations and high costs due to the need to manage cyanide waste.
3. Heap leaching
Heap leaching is suitable for low-grade or large chunks of oxidized gold ore, often without prior grinding.
After crushing, the gold ore is stacked on a leak-proof heap leaching pad, forming an ore pile. Cyanide solution is sprayed over the pile to dissolve the gold, which is then recovered from the leach solution.
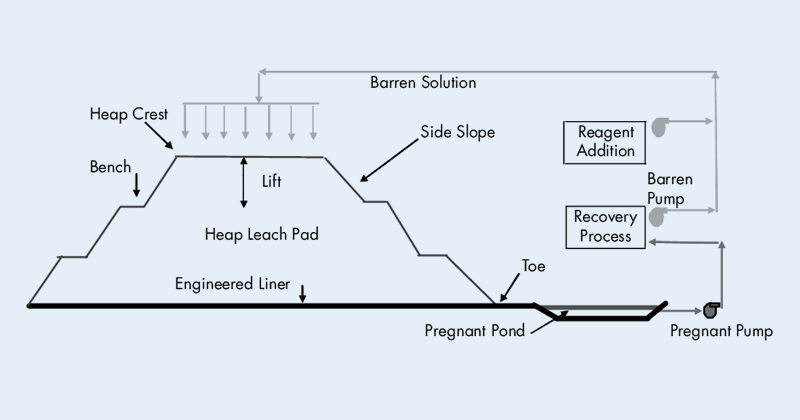
This process has low investment cost, simple operation, wide adaptability, and is suitable for large-scale extraction of low-grade gold ores. However, it requires specific ore particle size, as very fine particles may affect leaching efficiency.
These are the three main methods for processing oxidized gold ore. For partially oxidized ores, gravity separation and cyanidation are often combined. In fully oxidized ores, coarse gold is mostly recovered using gravity separation, while fine gold particles are treated with agitation cyanidation, and sand-sized particles are processed with percolation cyanidation.
Conclusion
The processing of oxidized gold ore depends on the ore's nature and the form of gold. By choosing the most suitable beneficiation methods and optimizing crushing, grinding, and separation processes, gold recovery rates can be maximized and economic benefits improved.
FTM Machinery is dedicated to providing processing solutions for various gold ores with advanced technology and equipment to help customers achieve more efficient and stable gold recovery. Contact us