The primary use of calcite lies in construction materials, particularly as a raw material for manufacturing cement and lime. It can produce calcium oxide (CaO) after calcination, which is one of the key components of cement clinker.
A world built by cement
Millennia ago, many pyramids in Egypt and Latin America were constructed using calcite minerals like limestone as fundamental building materials.
With the United Nations predicting that 68% of the world's population will reside in urban areas by 2050, there is a growing demand for infrastructure services in housing, transportation, energy, and more, to accommodate the expanding urban population.

In this context, the demand for calcite in the construction industry is particularly significant.
The role of calcite in cement production
1. Controlling cement composition and loss on ignition
Cement typically requires limestone (with calcite as the main component) containing a minimum calcium carbonate content of 75%. There are also specific limits on impurities such as SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and MgO to control the composition and loss on ignition of cement.

2. Enhancing cement setting performance
Calcite in cement accelerates the hydration process, producing more hydration products rapidly, thereby speeding up cement setting and reducing the occurrence of cracks and defects.

3. Maintaining Stability and Energy Efficiency
Calcite with high calcium carbonate content helps avoid issues of over-burning or incomplete reaction due to insufficient raw material purity, ensuring stability and energy efficiency.
4. Acting as a Fluxing Agent
During cement production, calcite acts as a fluxing agent, lowering the melting temperature of raw materials, thereby conserving energy and enhancing production efficiency.
These functions of calcite collectively ensure the performance and quality of cement products, meeting the construction industry's demand for high-performance cement.
How is calcite used in cement production? (Calcium carbonate processing plant)
The cement production process is commonly referred to as "two grinding and one calcination".
Here is an overview of cement manufacturing:
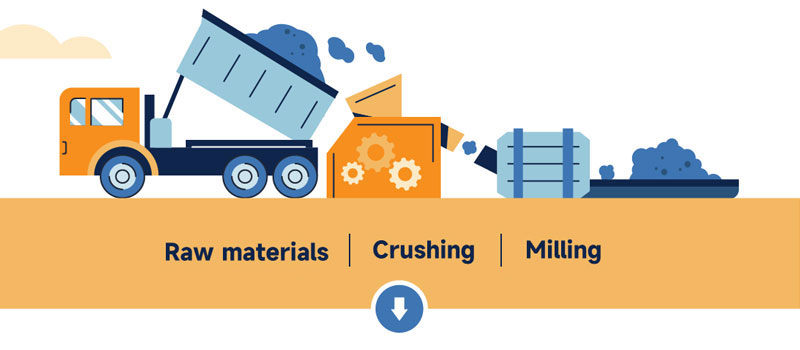
1. Raw materials like limestone and clay are crushed, mixed, and finely ground to obtain raw lime.
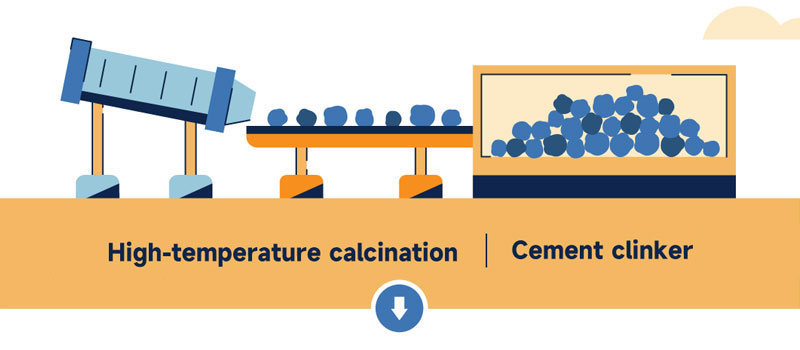
2. The raw lime is then subjected to high-temperature calcination to produce cement clinker.
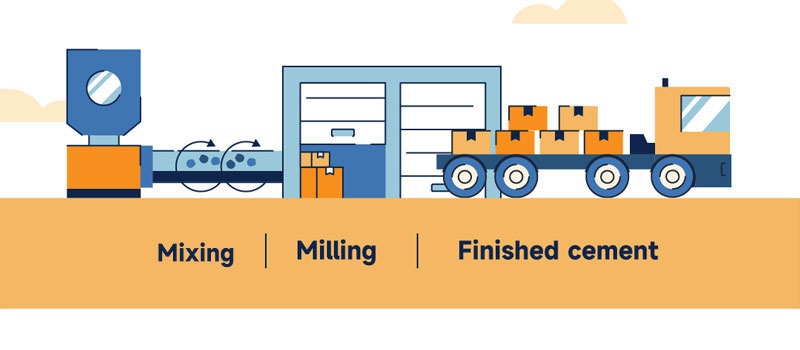
3. Cement clinker is further ground with gypsum and additives to produce finished cement, also known as Portland cement.
Let us take a tour of a cement processing plant in Russia, which produces 300 tons of finished cement per day, supported by equipment from FTM Machinery.
After understanding, the local cement industry is relatively close to raw material resources (rich in calcite ore), with convenient transportation and sufficient water resources.

Based on the actual situation, FTM Machinery's engineers have customized the following equipment for their cement production:Get a quote
Phase one: raw material grinding
Key equipment: Jaw Crusher, Ball Mill, Vertical Roller Mill

Limestone, clay, iron ore, and other raw materials are crushed by the jaw crusher into smaller particles and mixed in certain proportions.
The mixed raw materials are then finely ground into powder using a ball mill or vertical roller mill to obtain uniformly quality raw materials.
You might be interested in:
Phase Two: clinker calcination
Key equipment: Cyclone Preheater, Rotary Kiln
To accelerate combustion efficiency, the raw materials are first transferred to the cyclone preheater for preliminary heating, raising the temperature to above 500℃ to remove moisture and some volatile substances from the raw materials.

Subsequently, they are transferred back to the rotary kiln and calcined at temperatures between 1200°C and 1500°C until partially melted, resulting in granular cement clinker primarily composed of calcium silicate.
Phase three: cement grinding
Key equipment: Cement Mill, Cement Classifier
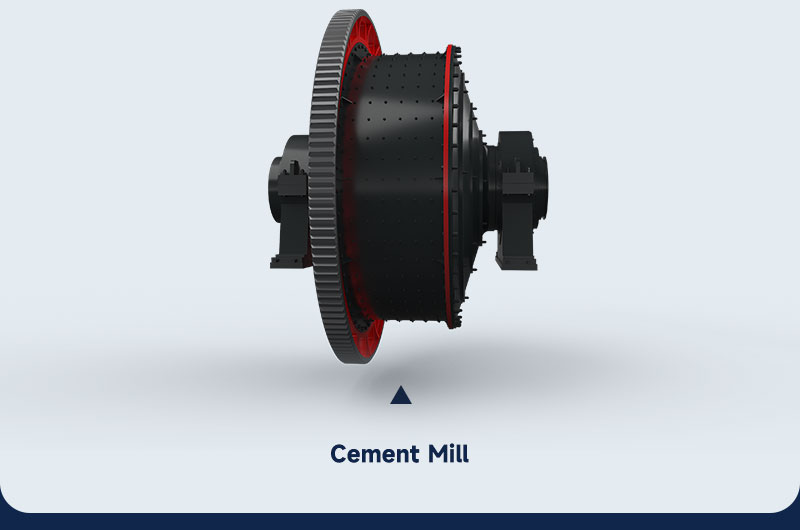

When the cement clinker cools to around 80℃, a suitable amount of gypsum, fly ash, slag, and other additives are added and sent to the cement mill for fine grinding.
Finally, the cement classifier filters out clumps or large particles from the powder, resulting in cement.
Phase four: cement packaging
Key equipment: Cement Packaging Machine
After setting the required weight, the cement packaging machine automatically fills the cement and completes a series of packaging processes such as sealing and label printing, greatly improving production efficiency.
Sustainability practices
Of course, in the entire cement production line, FTM Machinery also recommends equipping the factory with two pulse jet dust collectors in the grinding and packaging conveying sections to reduce dust flying and dispersion, protecting employee health, and reducing carbon footprint.
Seven factors affecting cement quality
For optimal cement performance, attention must be paid to the following aspects:
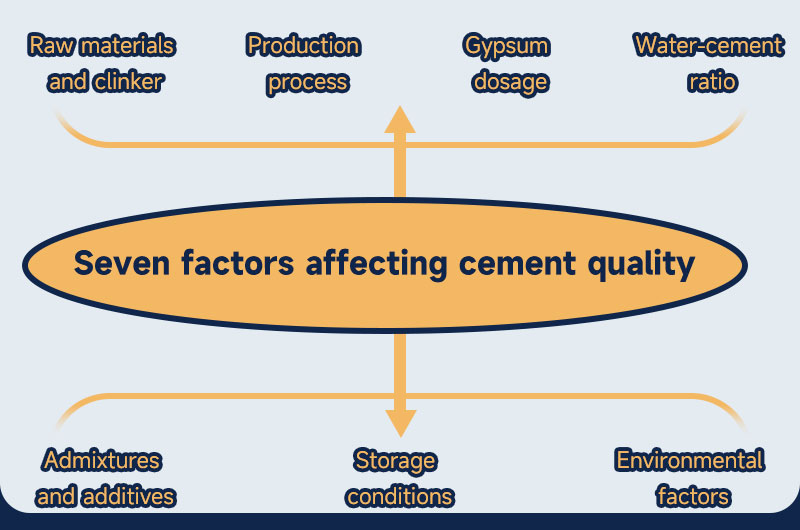
- Raw materials and clinker: The proportions of raw materials (limestone and clay) and the four main minerals in clinker (tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, tricalcium aluminate, and tetracalcium aluminoferrite) determine the curing speed and strength of cement.
- Production process: The calcination temperature and duration during production determine the quality of clinker; higher grinding fineness results in higher early strength of cement.
- Gypsum dosage: Added as a retarder to cement, its quantity needs precise control. Excess or insufficient amounts can affect cement's setting time and final strength.
- Water-cement ratio: Excessive water-cement ratio leads to decreased strength and crack formation; too low may affect construction workability.
- Admixtures and additives: Fly ash, slag, and various additives (such as accelerators, grinding aids) must be carefully selected and controlled to avoid adverse effects on cement quality.
- Storage conditions: Cement should avoid moisture and expiration, as dampness triggers premature hydration, reducing its effective components, while expired cement loses activity, impacting strength.
- Environmental factors: Low temperatures during construction delay the curing process, while high temperatures may lead to rapid water loss, affecting the quality of cement curing.
In summary, each stage from raw material selection to application can impact cement quality. Thus, controlling these factors is crucial for achieving desired performance.