What is a mineral processing plant?
A mineral processing plant is a place dedicated to processing ores, converting raw ores extracted from mines into high-grade mineral products or metals through a series of physical and chemical methods.
The main goal of mineral processing is to separate valuable minerals from waste rocks through efficient mechanical systems or chemical systems for further refining and use.

A typical mineral processing plant is able to process various types of ores and mineral materials, including metal ores, non-metallic ores, clay minerals, building materials and energy minerals.
- Metallic ores: Gold ore, silver ore, copper ore, lead ore, zinc ore, tin ore, and more.
- Non-metallic ores: Quartz, silica sand, feldspar, fluorite, limestone, and others.
- Clay minerals: Such as kaolin and bentonite.
- Building materials: Marble, granite, sand, and gravel.
- Energy minerals: Such as coal and uranium ore.
These mineral processing plants utilize advanced equipment and technologies to perform crushing, grinding, flotation, magnetic separation, gravity separation, and other processes, ensuring optimal mineral recovery rates and product purity.
Understanding the four stages of mineral processing
Mineral processing, also known as ore dressing or mineral beneficiation, typically consists of four key unit operations: comminution, sizing, concentration, and dewatering.
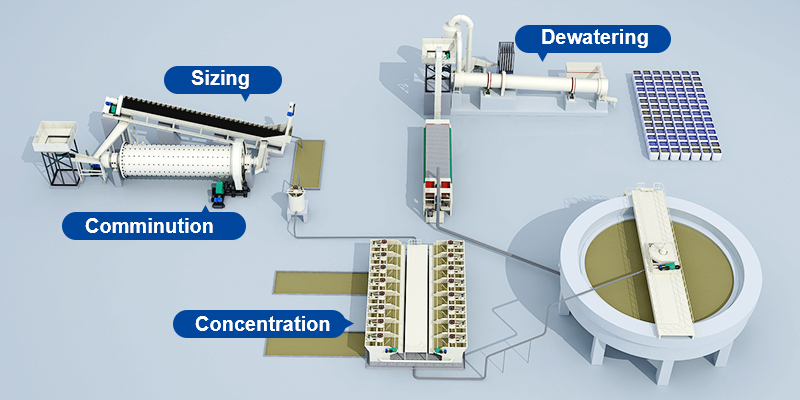
1. Comminution
Comminution involves both crushing and grinding. As the first step in mineral processing, comminution is to process large pieces of ore into smaller pieces with the help of crushers and grinders.
2. Sizing/Screening
Sizing refers to the process of separating ore particles based on their size. The most basic sizing method is screening, which involves passing rock pieces through one or more screens to sort them by size.
3. Concentration
Concentration is the core step in mineral processing. Its purpose is to separate valuable mineral components from waste rock or gangue, removing unwanted impurities.
The most common concentration methods in mineral processing include gravity separation, flotation separation, and magnetic separation.
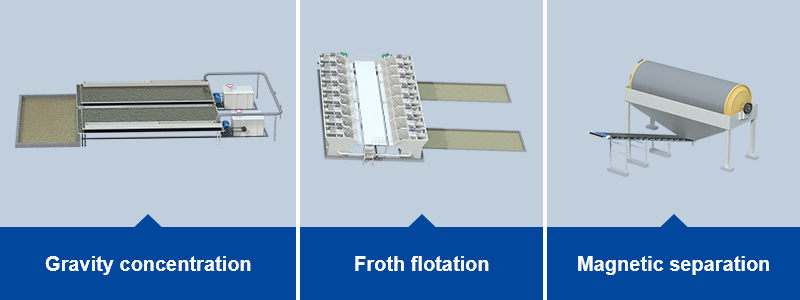
- Gravity concentration: This method separates minerals based on their differences in specific gravity. It is effective for separating heavier minerals like tungsten, tin, titanium, gold, platinum group metals, as well as iron and manganese.
- Froth flotation: This technique separates minerals based on their ability to attach to air bubbles. It is commonly used for the separation of copper, lead, gold, graphite, sulfur, and other minerals.
- Magnetic separation: Magnetic separation leverages differences in magnetic properties of minerals. As the slurry passes through a magnetic field, magnetic minerals are attracted, while non-magnetic minerals remain unaffected. It is often used for separating minerals such as iron ore, titanium ore, and chromite.
4. Dewatering
Dewatering is crucial in mineral processing, as it prepares ore for further processing and transport. Beneficiated concentrates typically have high moisture content, which is reduced through filtration, drying, and other methods to achieve a lower water content.
What equipment do mineral processing plants need?
Mineral processing plants are industrial bases that efficiently convert ores into useful minerals and metals. The operation of these plants depends on different types of processing equipment.
1. Crushing equipment
The crushing process of mineral processing plants is usually carried out in the order of primary, secondary, tertiary, or even quaternary crushing.
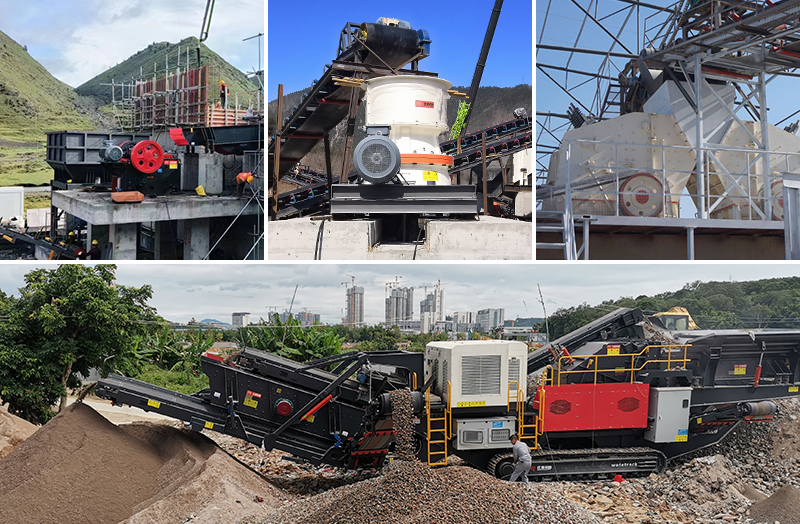

For primary crushing, jaw crushers are usually selected, which are suitable for hard and abrasive materials, especially for processing wet ores.
For secondary and tertiary crushing, cone crushers and impact crushers are commonly used. Cone crushers are suitable for rocks with medium hardness or above, and can produce high-quality stones with low needle-like content. Impact crushers are more suitable for medium-hard and brittle rocks, and can produce excellent cubic stones.
Combining crushing and mobility, mobile crushers are well-suited for in-situ crushing at mining or construction sites. They reduce transportation costs and can perform coarse, medium, and fine crushing with a single unit.
| Equipment | Parameters |
| Jaw crusher | Max. feed size: 1,200 mm, capacity: 105–1,590 t/h |
| Cone crusher | Max. feed size: 450 mm, capacity: 85–2,181 t/h |
| Impact crusher | Max. feed size: 800 mm, capacity: 60–2,000 t/h |
| Mobile crusher | 50 t/h, 100 t/h, 150–200 t/h, and 300 t/h |
2. Grinding equipment
Grinding is an important part of mineral processing, which aims to further grind the crushed ore to the ideal particle size in order to release the valuable minerals in the ore.

| Grinding equipment | Applicable materials | Advantages | Energy Consumption |
| Ball mill | Various ores, from hard to soft | Widely used for fine grinding; can operate in dry or wet modes based on process requirements. | High |
| Rod mill | Larger-sized ores | Ideal for coarse ore grinding, preventing over-grinding. | Low |
| Autogenous mill | Very hard, highly abrasive large ores | Uses the ore's impact for grinding, reducing wear on equipment and grinding media. | Low |
Dry grinding reduces the material to a qualified fineness of ore powder, commonly used for hard stones like silica sand and quartz. It is suitable for areas where moisture control is necessary or where water resources are scarce.
Wet grinding produces a slurry with a certain concentration (generally 60%–70%). It is suitable for processes requiring fine grinding as it more effectively releases valuable minerals from the ore.
3. Mineral processing equipment
Mineral processing equipment is the core of mineral processing and is used to separate valuable minerals from gangue or waste rock. Different mineral processing equipment separates minerals by physical, chemical or electromagnetic methods.

Flotation machine: The flotation machine separates minerals by using mechanical agitation and the buoyancy of bubbles. Minerals attach to the bubbles and float to the surface of the liquid for separation. Although flotation machines require fine grinding and can be costly, they are efficient and can process most types of ore.

Magnetic separator: Magnetic separators come in two types: dry and wet. Dry magnetic separators do not need water or liquid, making them simpler and cheaper to maintain, and more eco-friendly. Wet magnetic separators operate with water or liquid, extending the separation process and increasing the concentrate grade by 2%–4%.

Shaking table: The shaking table uses precise horizontal vibrations and water flow to separate minerals based on density, with large processing capacity and low cost. It is especially good for concentrating fine metal minerals like gold, tin, and tungsten, ensuring high purity in mineral recovery.

Spiral chute: The spiral chute uses gravity and centrifugal force to separate minerals. It is an ideal choice for fine-grained mineral separation and is widely used in gold, iron, titanium, etc.
4. Screening equipment
Screening equipment is used in a mineral processing plant to classify ore particles at different processing stages, ensuring that the size of the ore being handled is suitable for each stage, which improves processing efficiency and product quality.
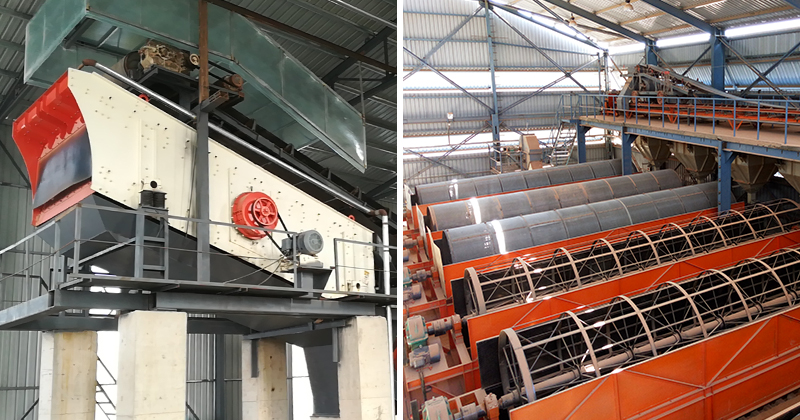

- Vibrating screen: Separates ore by size using high-frequency vibrations. It is used for screening crushed ore and grading final products. Screens can have one or more layers depending on the required material sizes.
- Trommel screen: Often used for wet screening, the drum screen feeds ore into a rotating drum. It is suitable for handling ores with high mud content.
5. Drying equipment
In addition to being used for drying ores, drying equipment can also be used for drying other materials.
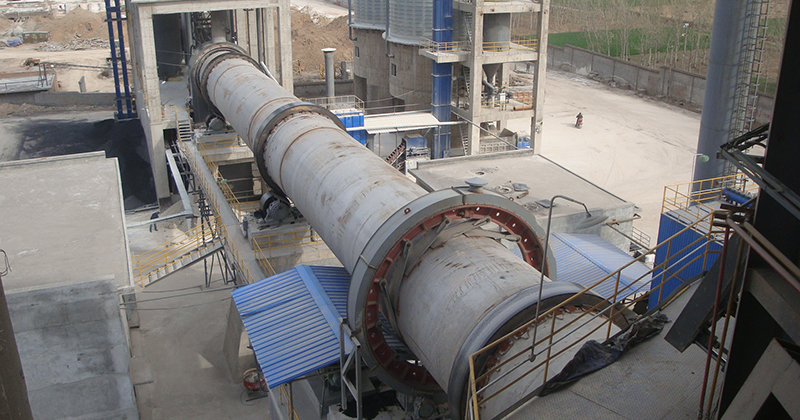

- Filter: Removes moisture from concentrates through pressurized filtration, suitable for the initial dehydration of various minerals. The filter cake has a low moisture content, which helps the subsequent drying process.
- Dryer: Common drying equipment includes rotary drum dryers and airflow dryers. This equipment can effectively reduce the moisture content of mineral concentrates. In addition, they are widely used to dry other materials such as river sand, quartz sand, and clay.
6. Auxiliary equipment
Auxiliary equipment supports the smooth progress of the entire processing process in mineral processing plants.
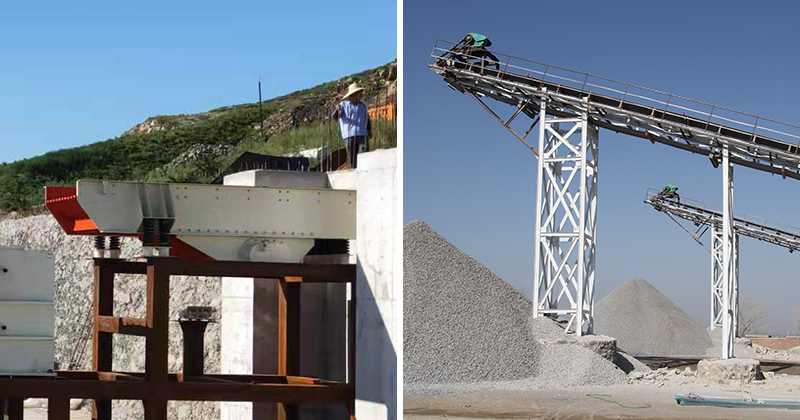

- Feeder: Such as vibrating feeder, responsible for evenly and continuously feeding ore into crushing or grinding equipment to ensure stable operation of the equipment.
- Conveyor belt: Used to transport ore and concentrate between various processing stages, usually with multiple belt conveyors and bucket elevators to ensure the continuous flow of materials.
Exploring real cases of gold processing plants
In Africa, gold processing is not only a blend of technology and craftsmanship but also a cornerstone of national economies. Discover how countries have successfully increased their gold production through effective processing.
Gold processing plants in Nigeria, South Africa, and Tanzania
FAQs
How many tons of material can a mineral processing plant handle per day?
Small plants might process dozens to hundreds of tons daily, while large plants can handle thousands of tons. The exact capacity depends on the equipment configuration, process design, and ore characteristics.
How much does it cost to set up a mineral processing plant?
Setting up a mineral processing plant involves costs for equipment procurement, operation, and maintenance. Start-up costs for small plants can range from hundreds of thousands to a few million dollars, while large projects may require tens of millions or even hundreds of millions of dollars. These estimates are influenced by factors like scale, technology, and location, and actual costs may vary significantly based on market conditions and specific project details.
What is the return on investment period for a mineral processing plant?
The ROI period depends on the type and value of the ore, processing capacity, equipment investment, and operating costs. While large plants might take longer to achieve ROI, using efficient equipment and optimizing processes can accelerate this timeline.
Establishing an efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly ore processing plant is a complex task. With experienced engineers and technical experts, FTM Machinery provides comprehensive, customized mineral processing solutions. Choose FTM Machinery as your reliable partner for success. Contact us