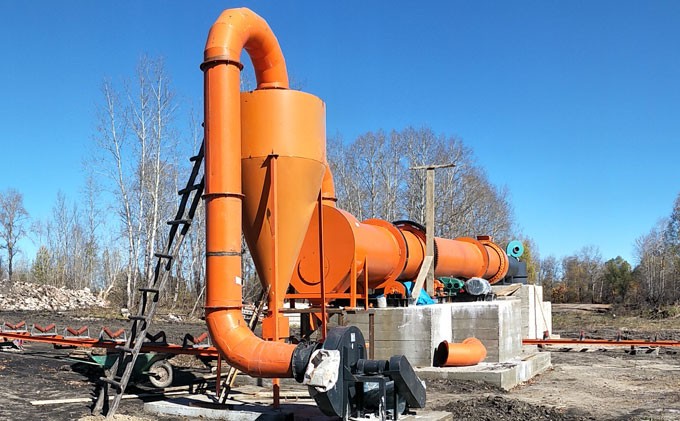
Rotary drum dryers are widely used industrial dryers that use advanced drying drum technology to quickly dry high-moisture solid materials through direct or indirect heating to achieve efficient heat and mass transfer.
As one of the leading rotary dryer manufacturers, FTM Machinery has manufactured various types of drum dryers to meet the drying needs of wet materials such as coal, minerals, cement, and fertilizers.
What materials can be dried?
Rotary drum dryers are widely used in construction, agriculture, industry and mineral processing. It is an ideal drying equipment for various powdered and granular materials such as sand, minerals, cement, coal, chemical powder, fertilizer, sawdust, etc.
Regardless of the initial moisture content, it can dry efficiently, with a maximum temperature of 800℃ without damaging the material, and the final moisture content can be reduced to 0.5%–1%.
1. Construction materials
The rotary drum dryer can dry construction and engineering raw materials, mainly natural sand (such as river sand, yellow sand, sea sand, etc.), manufactured sand (such as silica sand, quartz sand, glass sand, dolomite sand, etc.), aggregate, cement, clay, blast furnace slag, gypsum powder, etc.

2. Biomass materials
The drum dryer can dry biomass materials such as sawdust, wood chips, distillers' grains, straw, alfalfa, wood shavings, bagasse, cocopeat, chemical fertilizers, organic fertilizers, wine dregs, potato dregs, fruit dregs, egg shells, shells, cow bones, etc. Some farmers may call this dryer a “rotary biomass dryer”.

3. Industrial materials
The drum dryer can dry industrial products or by-products, such as slag, steel slag, fly ash, industrial sludge, pond ash, phosphate, tailings, barium chloride, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, petroleum coke, desulfurized gypsum, calcium carbonate, active lime, etc.

4. Minerals and ores
The rotary drum dryer is widely used in the mining and coal industry. It can process various mineral and ore products after mining.

- Metal ores: iron ore, manganese ore, copper ore, laterite nickel powder, gold ore, limonite, lithium ore, etc.
- Non-metallic minerals: quartz, limestone, slag, bentonite, shale, diatomite, phosphate rock, clay, fluorite, feldspar, etc.
- Coal: coal, coal gangue, coke, charcoal, anthracite, coal slime, coal slurry, lignite, cinder, coal flotation concentrate, mixed cleaned coal, carbon black pellets, gas coal, etc.
Types of rotary drum dryers
FTM Machinery engineers have designed and manufactured direct and indirect dryers based on more than 40 years of rotary drum drying experience.
Direct rotary dryers are the preferred drying method and are more efficient. The main difference between them and indirect rotary dryers is how heat is transferred to the material.
Direct dryers rely on convective heat transfer from direct contact between the material being processed to the combustion gases to dry the material efficiently. However, indirect dryers rely on heat transfer through the drum shell wall via conduction.
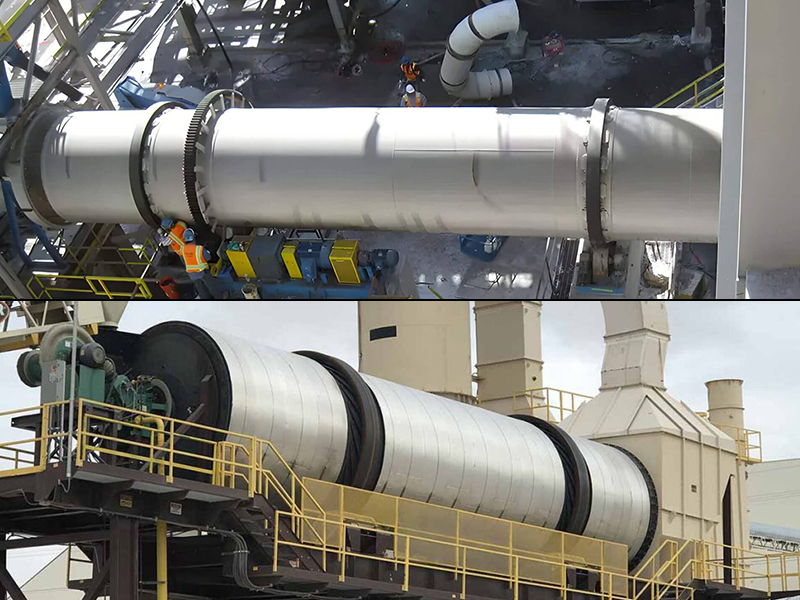

When drying materials in an inert atmosphere (such as sterile products or ultrafine materials), indirect dryer equipment can avoid the risk of solids becoming entrained in the gas flow and ending up in the exhaust gas system.
Hot-selling models of rotary drum dryers:
| Spec./m(Dia.×Length) | Capacity(t/h) | Highest Inlet Air Temperature(℃) |
| Φ1.2×8.0 | 1.9–2.4 | 700–800 |
| Φ2.2×12 | 9.7–12.2 | 700–800 |
| Φ2.4×22 | 21.2–26.5 | 700–800 |
| Φ3.6×28 | 60.8–76.0 | 700–800 |
Rotary drum dryer diagram/design
The drum dryer equipment has a simple structure, mainly including the thermal system, feeding device, drum body, material lifting device, transmission gear, supporting device, sealing device, and outlet. It is easy to operate and repair in case of failure.
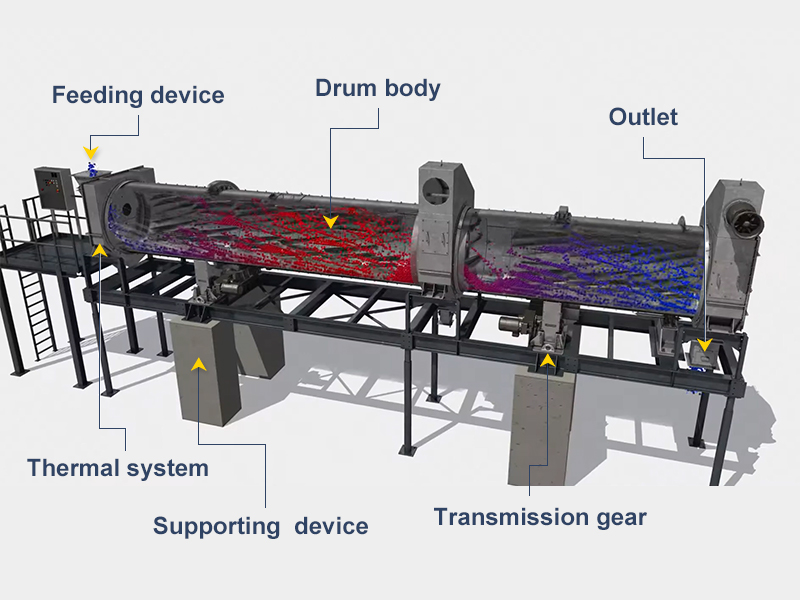

1. Drum body
The rotary drying drum uses high-grade alloy steel plates for superior heat and pressure resistance.
Its wear resistance is improved by 3-5 times, and its service life is extended by more than 3 times. The dryer runs smoothly and reliably.

2. Multi-module material lifting device
This device lifts the material to increase airflow contact, boosting the drying rate and aiding material movement.
This eliminates the wind tunnel effect of traditional dryers, improving thermal efficiency and reducing coal consumption by about 20%.

3. Transmission gear
This device features an adjustable tug structure and multiple lubrication methods.
It works well with the rolling ring so that it can reduce wear, preventing shaft breaks, extending its lifespan, and shortening the replacement cycle.

4. Automatic control
All automatic controls for the firing system are available to easily and safely control fuel flow, ignition, temperature and flame air.
Direct or indirect firing can be performed using any type of fuel or gas.
Why choose FTM Machinery rotary drum dryers?
- High drying efficiency: Up to 80% thermal efficiency with intense evaporation from high-temperature flue gas.
- Materials will not stick to the wall: This rotary dryer can effectively dry sticky materials and prevent materials from sticking to the wall.
- Adjustable output: Continuous operation with a large drying capacity of 1.9-76 t/h.
- Adjustable moisture & particle size: Final moisture and particle size can be adjusted. For example, coal can be dried to 8% moisture with a particle size of 8 mm.
- High quality & low drying cost: Strong overload resistance, reliable operation, less fuel consumption, and low drying costs.
- Eco-friendly: Balanced drum temperature and advanced dust control ensure zero pollution, turning exhaust gas into water vapor.
How does a rotary drum dryer work?
The wet material is sent to the hopper by a belt conveyor or bucket elevator and enters the feeding device through the feeding pipe of the hopper.
This video demonstrates the working principle of the drum dryer:
A slightly inclined, horizontal rotating drum with the material lifting device (shoveling plates) lifts the material, allowing it to cascade through hot air.
As the wet material moves forward in the drum, it directly or indirectly receives heat from the heating carrier, which dries the material before it exits through the discharge end. A pulse jet dust collector is often used to capture the material contained in the gas.
FAQs about rotary drum dryers
1. What kind of fuel does the drum dryer use?
-

- Coal, the most versatile and cost-effective fuel can be divided into bituminous coal and anthracite. It can generate heat of 5,000 kcal/kg. Drying equipment mostly uses anthracite, and dust removal and waste gas treatment are required after the drying process.
- Gas includes all combustible gases such as natural gas, biogas, and coal gas, with a calorific value of about 8,500 kcal/cubic meter. It has high combustion efficiency and low air pollution, but the overall cost is slightly higher than coal, and it is restricted by pipelines.
- Biomass fuel, promoted by the government in recent years, is made from wood raw materials like sawdust and straw pellets. Its calorific value can reach 3,000–4,500 kcal/kg. Its cost is slightly higher than coal, comparable to gas fuel, and is not restricted by pipelines.
2. How to choose the heat carrier of the rotary drum dryer?
- The heating carrier is determined by factors such as the nature of the material, whether it is allowed to be contaminated, etc.
- a. Flue gas: If the solid material being processed is not afraid of high drying temperature and is allowed to be slightly polluted, flue gas can be used as a heat carrier to obtain a higher volume evaporation rate and thermal efficiency.
- b. Hot air: It is used as the heat carrier if the processed material is not allowed to be contaminated. The air can be heated by steam heaters, electric heaters, other industrial waste gases, etc.
- c. Indirect heating of metal walls: If the dried material is not allowed to be contaminated and diluted by air, heat will be introduced through the cylinder wall, with flue gas passing outside the drum. The internal surface heat exchanger (center pipe, line pipe, sleeve, etc.) transfers heat via metal walls using flue gas, steam, or electric heating.
3. How is a rotary drum dryer different from a rotary kiln?
- Rotary dryers and kilns are similar in design but serve different purposes.
- a. Heating Objective: For drying materials, a rotary drum dryer (800ºF–1400ºF) is ideal. For chemical reactions or phase changes, a rotary kiln is used. Thus, the rotary kiln needs to be operated at a higher temperature (1000ºF–3000ºF).
- b. Lining: The direct-fired kilns are lined with refractory materials and bricks to protect the steel shell. However, indirect rotary kilns and rotary dryers are unlined and use shells made of a high-temperature resistant alloy to withstand the internal temperature.